Create and run a new experiment¶
Auptimizer only needs a modified training script and an experiment configuration file (.json) to run a new experiment.
Create the
experiment.jsonfile to specify the experiment configuration and hyperparameters. Usingpython -m aup.initwill guide you interactively. This json file structure is generally the same for most algorithms with minor modifications. See Configure HPO Algorithm for more details.Modify your training script. We provide three approaches for modifying the training script:
Your experiment is now ready to run via
python -m aup experiment.json. For more details, see Run experiment.
Terminology¶
For data science applications, the user (AI scientist/engineer) solves a given data mining problem with a specified machine learning model.
A script (code) is written and some hyperparameters are identified to be explored during model training.
Typically, the user carries out an experiment to examine a range of hyperparameter combinations and measures the performance of the model on a hold-out dataset. For example, testing a deep learning model by exploring the learning rate between 0 and 1, and dropout between 0.4 and 0.6. the performance is measured by accuracy.
Each individual training process for a given selection of hyperparameters (e.g., learning rate = 0.1, dropout = 0.5) is called a job.
All jobs run on an assigned computational resource, e.g. CPU, GPU. And after all jobs are finished, the user retrieves the best model from the training history for further analysis or application.
Manual modification of training code¶
If you plan to change your training script manually, the general flow of the conversion process is as follows:
parse the configuration file (first argument from command line, i.e.
sys.argv[1]) usingaup.BasicConfig.load(sys.argv[1]). And use the hyperparameters parsed from theBasicConfigin your code, such asconfig.param_nameorconfig['param_name'], whereparam_nameneed to be consistent with the one used inexperiment.json.to report the result by using
aup.print_result.Add Shebang line
#!/usr/bin/env pythonand make the script executable (chmod u+x script.py).
Code conversion with decorator¶
For better control, you can use aup_args or aup_flags to decorate your code. The examples are in below:
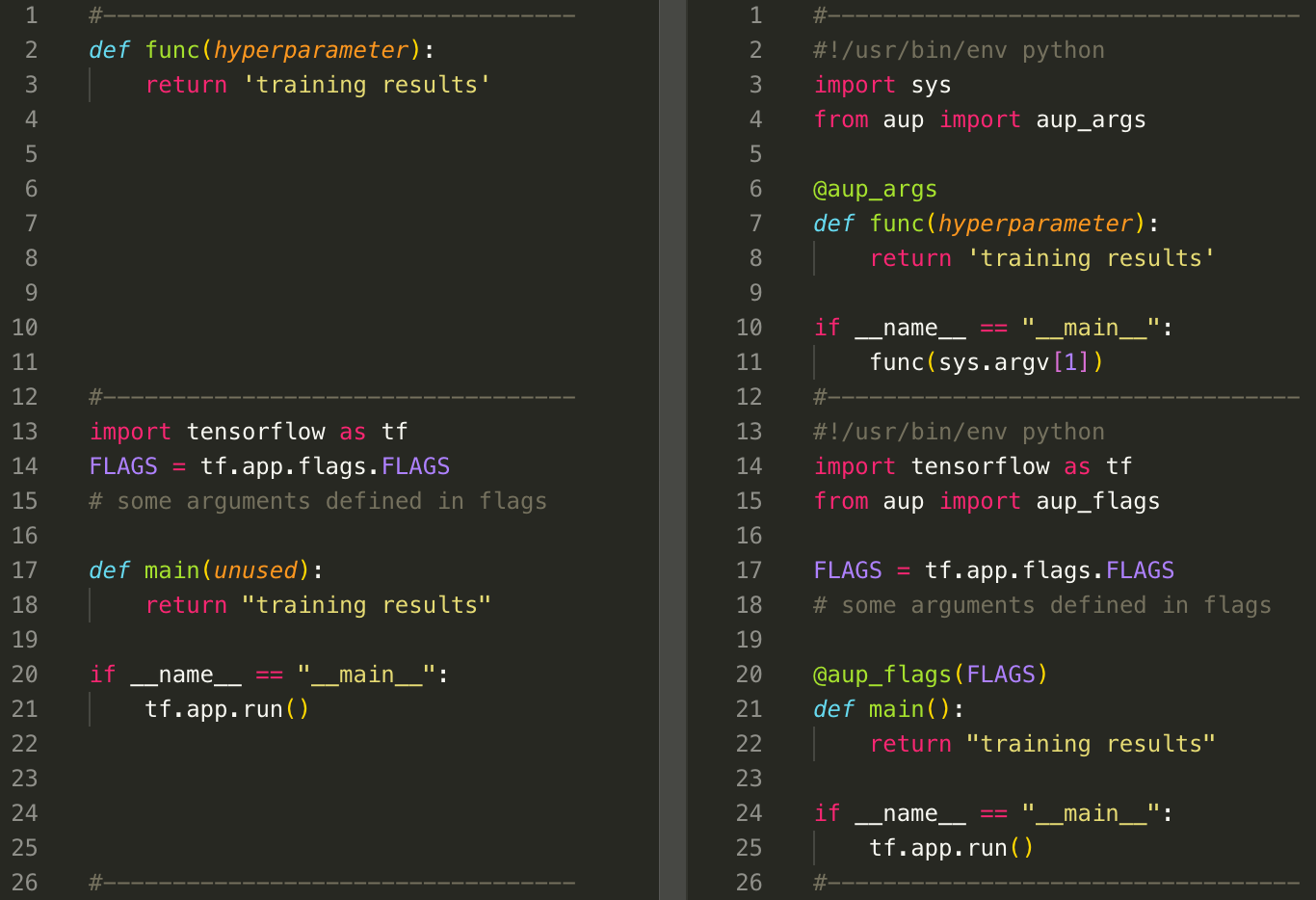
Example of using decorator for code conversion.¶
Auto code conversion¶
If your training function takes all hyperparameters as input, then Auptimizer converts code to run if the training script is well defined as follows:
python -m aup.convert <script> <exp_json> <func_name> -o [output]
scriptthe original script used for training, it must contain the function with namefunc_name. Also no “__main__” inside the script.exp_jsonexperiment configuration defined by the user. It must contain the hyperparameters used byfunc_name.func_namethe entry function used for training. It uses all hyperparameters defined inexp_json. All other inputs need to be optional and not overlapping with the hyperparameter names.outputoptional name for outputcode. If not specified, it creates a file with the name specified inexp_json.
Check out the folder Examples/2dfunc_diff_opt/README.md in the repository for example usage.
Run experiment¶
Once the experiment has been correctly set up, it is very easy to start the experiment:
python -m aup experiment.json
Additional arguments¶
--test: will run in test mode by executing one job--aup_folder: manually specify the.aupfolder--log: set log level to[debug,info,warn,error]--resume: path to a pickled file saved by a previous experiment, will resume experiment from previous saved proposer state--sleep: time delay for sequential jobs (avoid database collision)
Additional runtime configuration for Node/AWS¶
The user should either have Auptimizer installed on the remote machine, or at a minimum, copy the <repo>/src/aup.py script to the remote machine that can be imported by the jobs.
Additional configuration for node/AWS environment for runtime can be specified under the runtime_args in the experiment.json.
This is important for setting up the environment on the remote machine.
The specific arguments are:
prescript: any script to be run before the job. (use ; to separate different commands)postscript: any script to be run after the job.overwrite: remove the existing job file if exists. Otherwise, it will use the existing file on the node.env: other environment variables, listed as dictionary {“CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES”:”0”}
Other resource-related arguments are under resource_args:
reconn_wait_time: number of seconds to wait if SSH open connection is broken, before reconnecting. Default is 30 (seconds).max_retries: number of retry attempts, with ‘reconn_wait_time’ seconds before the job is tagged as failed. Default is 3.async_run: whether to run the job asynchronously on the remote instance. This will allow Auptimizer to run the job on the instance and check periodically for completion, instead of maintaining an open connection. Default is False (boolean).async_reconnect: number of seconds to wait and reconnect to check job status of async job. Default is 30 (seconds).async_timeout: total number of seconds to wait from async job start before the job is tagged as failed and discarded. Default is None (seconds).shutdown: turn off AWS instance after Experiment finishes. (only for AWS)connection_retry: If starting a stopped instance, AWS connections attempts might fail initially. This variable controls the number of retry attempts every 30 seconds. Default is 10 (only for AWS).
See Examples/2dfunc_diff_res/ for more examples of experiment json files.
Results / further analysis¶
The output of an experiment is saved in two places:
jobs/folder contains the configuration of each job in<job_id>.jsonand output of each job in<job_id>.out..aup/sqlite.dbdatabase file contains the experiment history (configurations and results). All jobs for different experiments are all saved under unique IDs, unless it has been reset.